Maxwell equation in integral form YouTube
Maxwell's equations are a set of four differential equations that form the theoretical basis for describing classical electromagnetism: Gauss's law: Electric charges produce an electric field. The electric flux across a closed surface is proportional to the charge enclosed. Gauss's law for magnetism: There are no magnetic monopoles. The magnetic flux across a closed surface is zero.
PPT Maxwell’s equations PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1461021
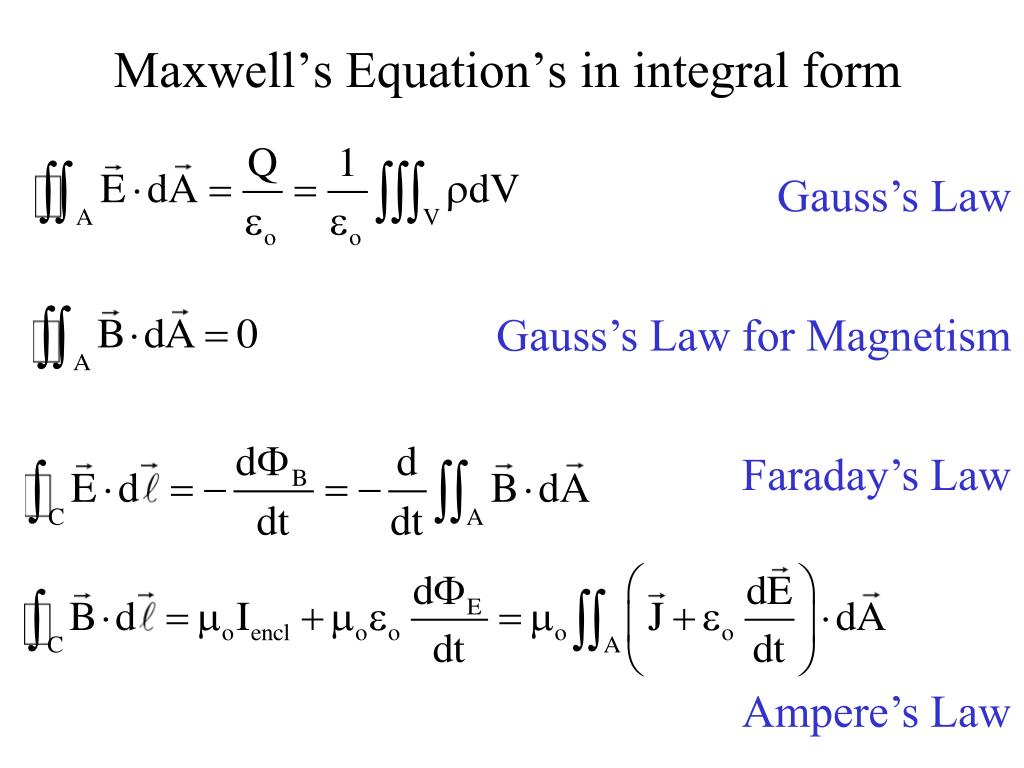
Maxwells Equations - Closed Surface with Enclosed Charge. For a closed system, the enclosed charge is the product of the surface integral and the electric flux density.. It can be mathematically represented as: ∯ \(\overrightarrow{D}.d\overrightarrow{s}= Q_{enclosed}\) ---- (1) Closed systems have only volumes so converting surface integrals to volume integrals by using divergence of vectors:
PPT Maxwell’s Equations PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1322316
In equation ( 1.1 ), is the induced electric field (in units of V m −1 ), is the magnetic flux density, or magnetic inductance (in units of Tesla, or kg s −1 A −1 ), the left-hand side integral is along a closed path, while the right-hand side is over an area . The integral on the right-hand side denotes the magnetic flux, where is the.

Fond memories... Maxwell's equations.... (which I prefer in integral form over differential form)
Learn the basics of Maxwell's equations, the fundamental laws of electromagnetism, in this lecture from the US Particle Accelerator School. You will understand the sources and properties of electromagnetic fields, the differential and integral forms of the equations, and the concepts of phase and group velocity.

Maxwell's Equations Integral Form Poster Zazzle
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell-Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, electric and magnetic circuits. The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, wireless.

Maxwell's Equations Integral Form Poster Personalized prints, Equations, Custom
from Office of Academic Technologies on Vimeo.. 9.12 Maxwell's Equations Differential Form. Let's recall Maxwell equations. In integral form, we have seen that the Maxwell equations were such that the first one was Gauss's law for electric field and that is electric field dotted with incremental area vector dA integrated over a closed surface S is equal to net charge enclosed in the.

How Maxwell's Equations are Defined for Electrostatics and EEVibes
The electric field E E → corresponding to the flux ΦE Φ E in Equation 16.3 is between the capacitor plates. Therefore, the E E → field and the displacement current through the surface S1 S 1 are both zero, and Equation 16.2 takes the form. ∮C B ⋅ ds = μ0I. ∮ C B → · d s → = μ 0 I. 16.5.
Maxwell’s Equations (free space) Integral form Differential form MIT 2.71/2.710
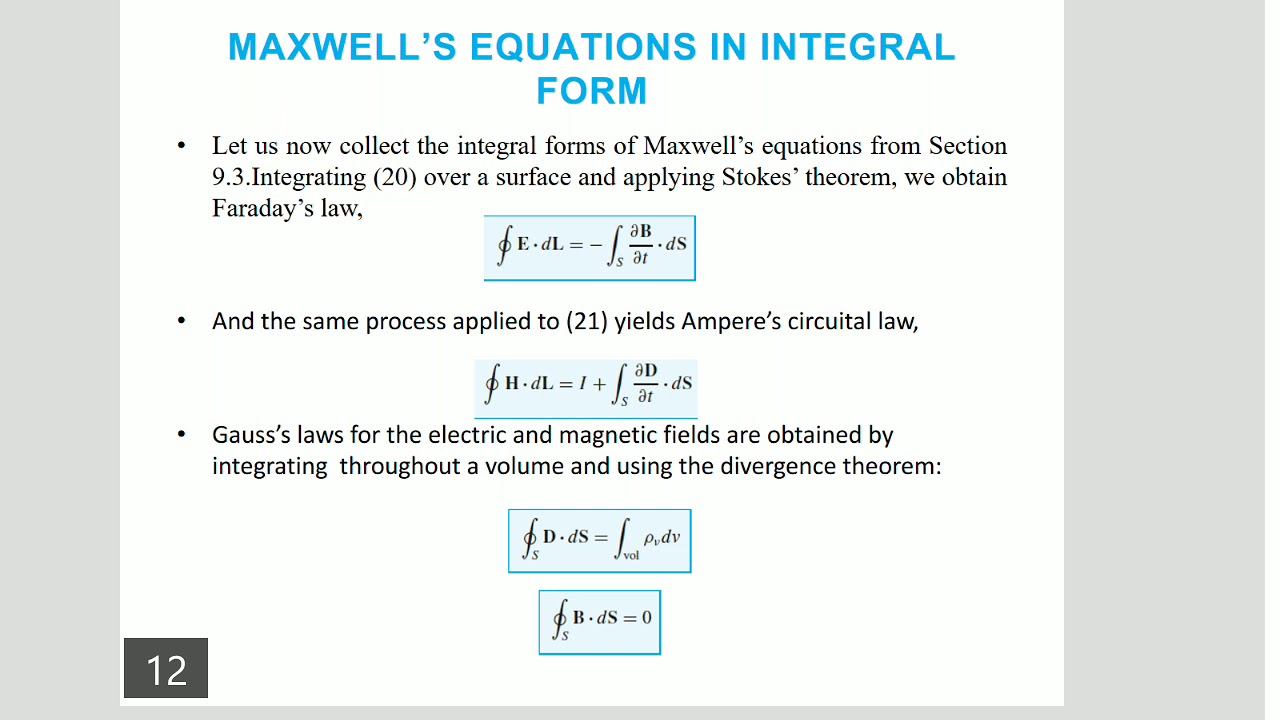
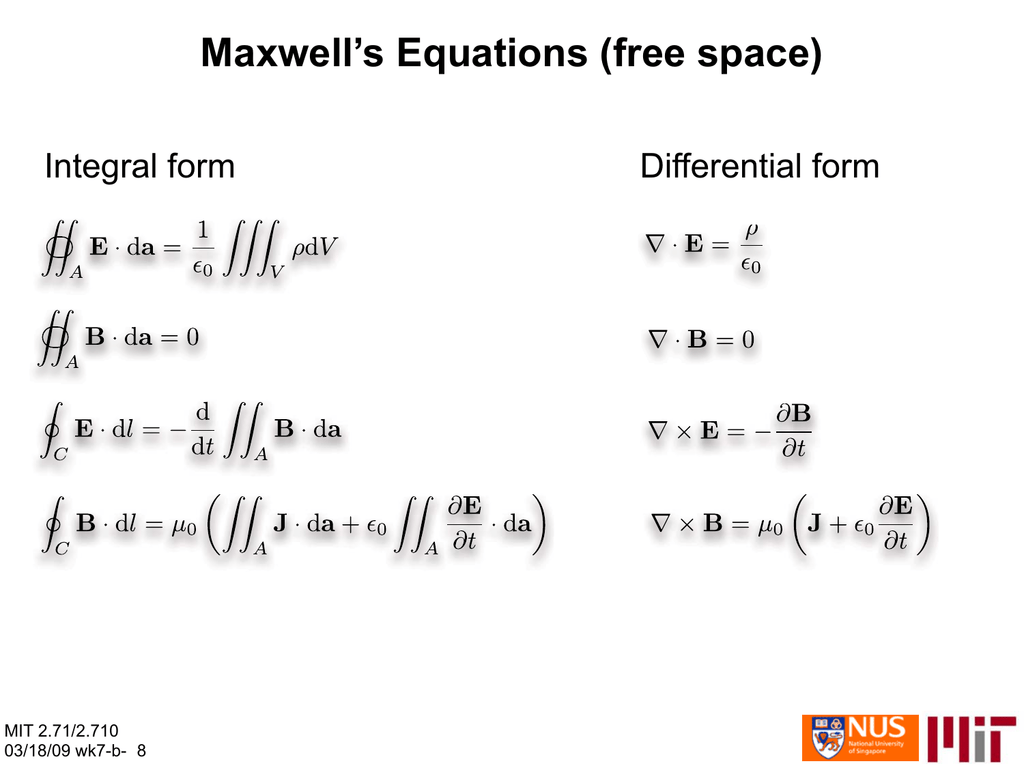
Maxwell's equations in integral form. The differential form of Maxwell's equations (2.1.5-8) can be converted to integral form using Gauss's divergence theorem and Stokes' theorem. Faraday's law (2.1.5) is: ∇ × ¯ E = − ∂¯ B ∂t. Applying Stokes' theorem (2.4.11) to the curved surface A bounded by the contour C, we obtain:

"Maxwell's Equations Integral Form" Poster by PhysicsThisWeek Redbubble
Application of Vector Calculus. To this point, we have derived three fundamental theorems of advanced calculus: Green's theorem on circulation and vorticity in two dimensions,
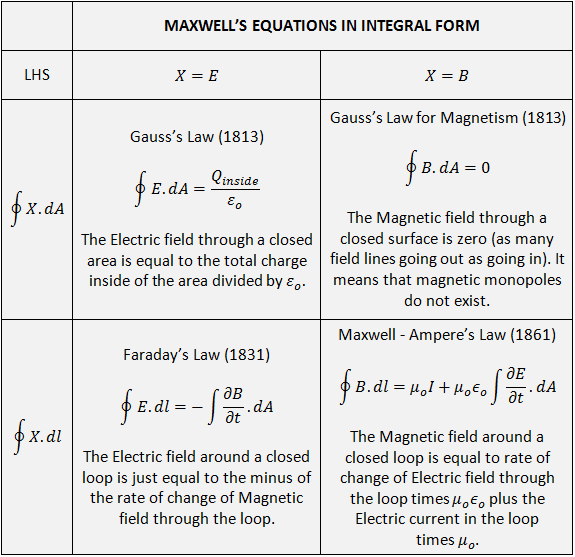
Maxwell’s Equations in Integral Form RAYmaps
Maxwell's equations represent one of the most elegant and concise ways to state the fundamentals of electricity and magnetism. From them one can develop most of the working relationships in the field. Because of their concise statement, they embody a high level of mathematical sophistication and are therefore not generally introduced in an.
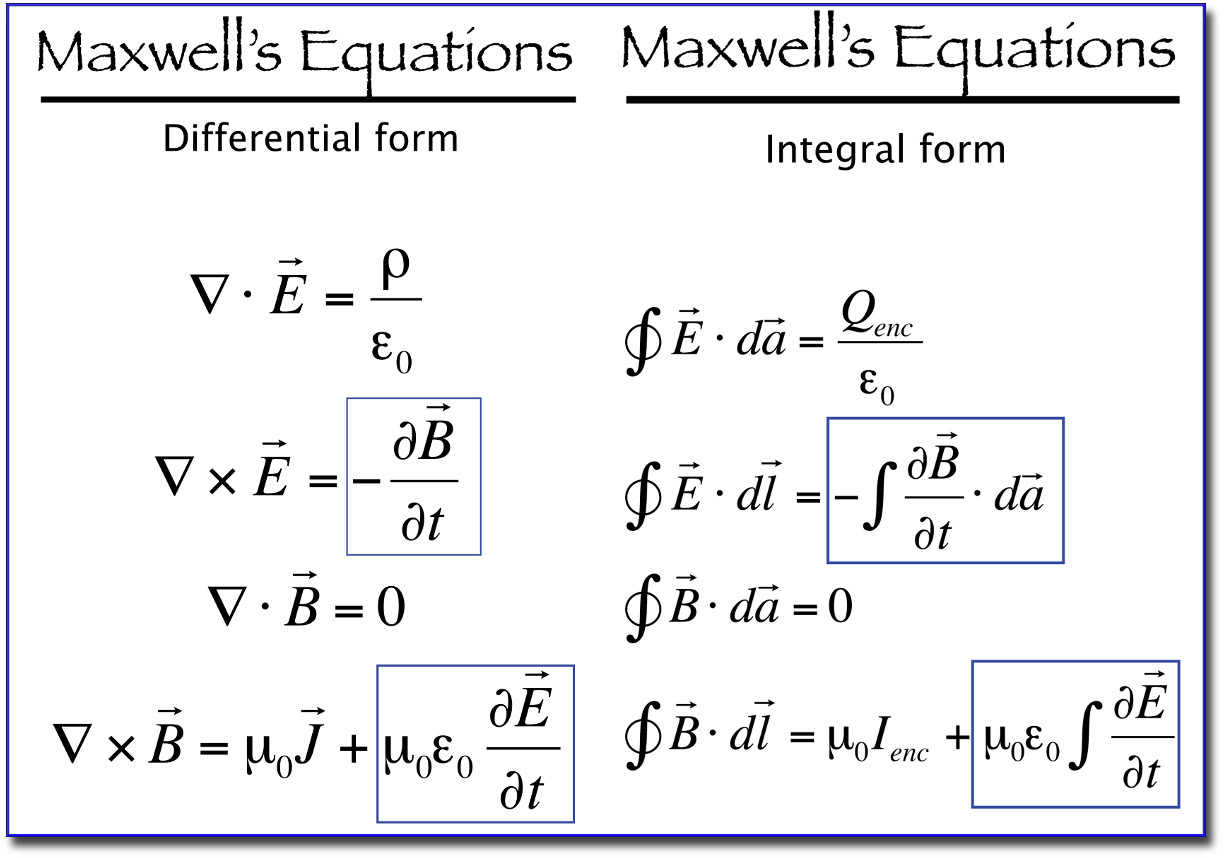
Origini delle equazioni di Maxwell tra genio e follia
Maxwell Third Equation. Statement: Time-varying magnetic field will always produce an electric field. Maxwell's 3rd equation is derived from Faraday's laws of Electromagnetic Induction.It states that "Whenever there are n-turns of conducting coil in a closed path placed in a time-varying magnetic field, an alternating electromotive force gets induced in each coil."
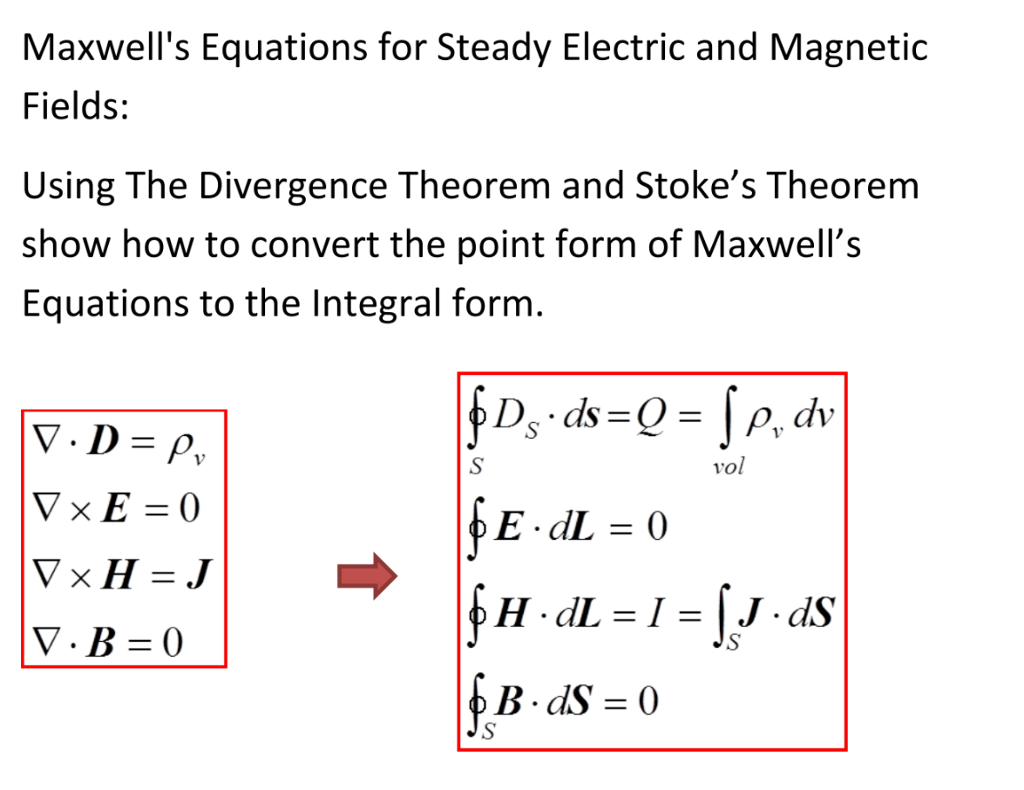
Solved Maxwell's Equations for Steady Electric and
Maxwell's equations, four equations that, together, form a complete description of the production and interrelation of electric and magnetic fields. The physicist James Clerk Maxwell, in the 19th century, based his description of electromagnetic fields on these four equations, which express experimental laws.

"Maxwell's Equations Integral Form" Spiral Notebook by PhysicsThisWeek Redbubble
Lecture notes on Maxwell's equations in integral form in free space, Ampere's law, Gauss' law for electric field and magnetic field, conservation of charge, and Lorentz force law.

Maxwell's Equations in Integral Form Poster Physics Posters
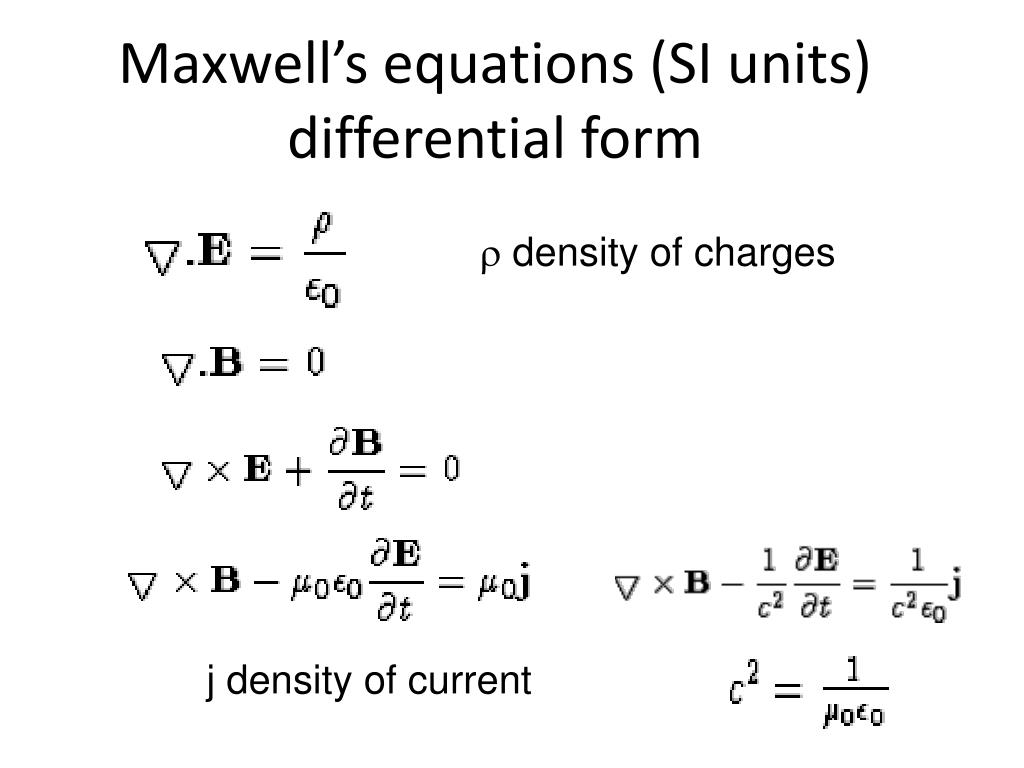
15.11: Maxwell's Equations in Potential Form. In their usual form, Maxwell's equations for an isotropic medium, written in terms of the fields, are. together with D = ϵ E and B = μ H, we obtain for the first Maxwell equation, after some vector calculus and algebra, (15.11.7) ★ ∇ 2 V + ∂ ∂ t ( div A) = − ρ ϵ. For the second.

"Maxwell's Equations Integral Form" Poster by PhysicsThisWeek Redbubble
40 Chapter 2 Maxwell's Equations in Integral Form For convenience, we shall divide the path into ten segments having equal widths along the x direction, as shown in Figure 2.2(a).We shall number the segments 1, 2, 3, 10.The coordi- nates of the starting and ending points of the jth segment are as shown in Figure 2.2(b).The elec- tric field at the start of the jth segment is given by
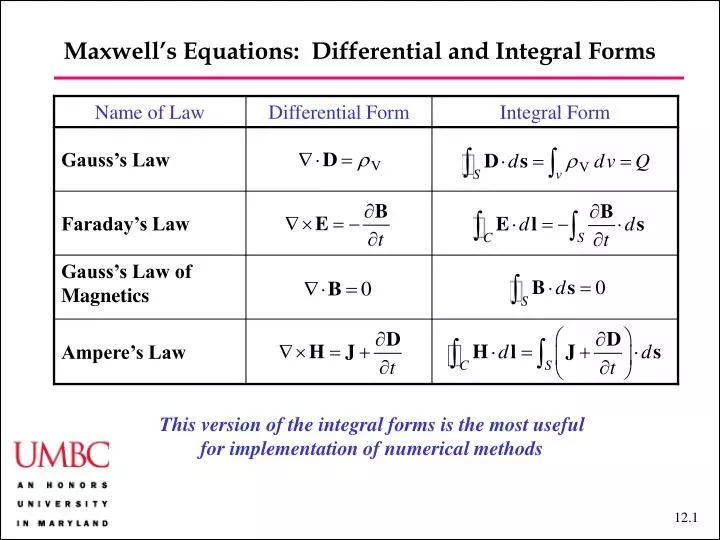
PPT Maxwell’s Equations Differential and Integral Forms PowerPoint Presentation ID2182643
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Maxwell's Equations Electromagnetic wave propagation is described by particular equations relating ve vector elds E, D, H, B, J and the scalar eld ˆ, where E and D denote the electric eld